Lab for Energy & Environment in the Asia-Pacific (LEEAP)
Responding to climate change requires deploying low-carbon technologies rapidly and at scale while reducing emissions from technologies that meet the bulk of global energy demand today. At the same time, the characteristics of technologies used to supply energy services globally differ markedly, with implications for the structure of supply chains, and for effective policy mixes. At LEEAP we adopt a technology-specific approach to describing and analysing the low-carbon energy transition.
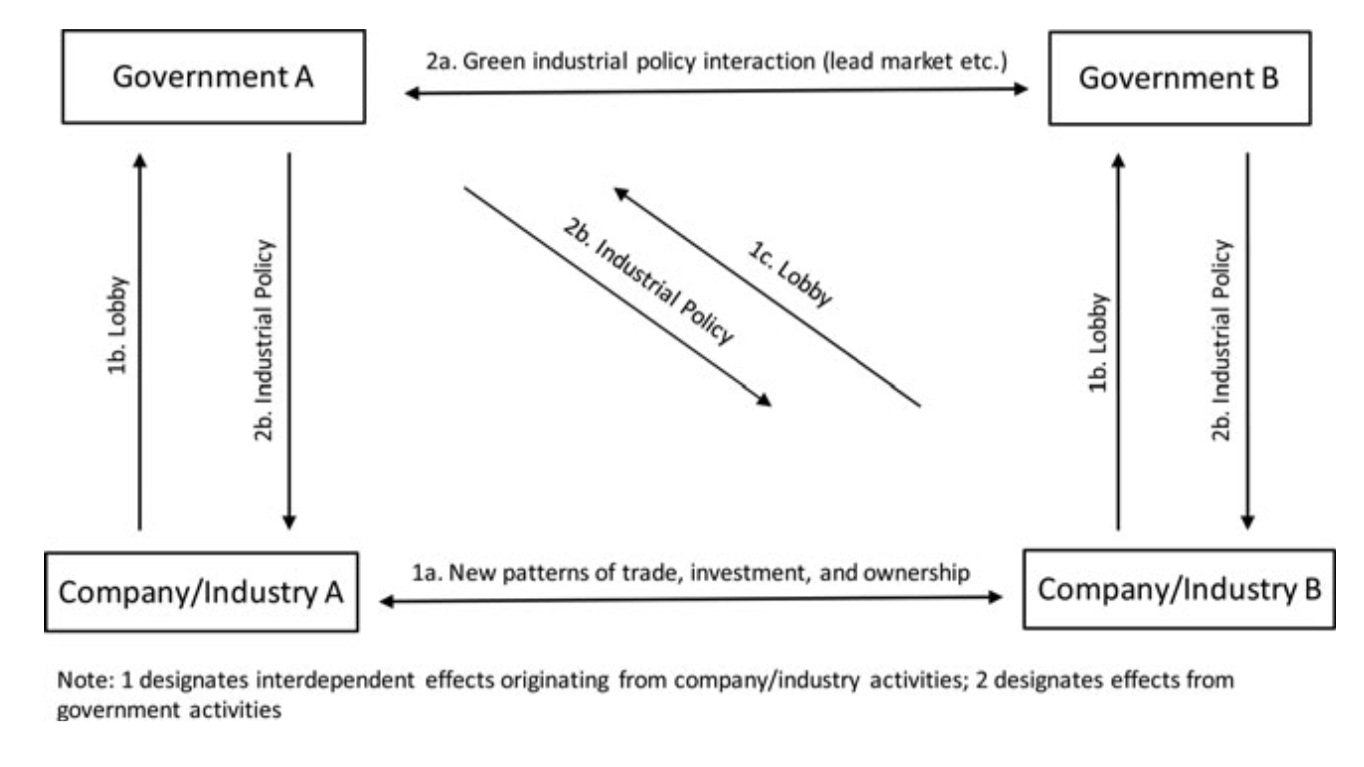
Our approach is problem-driven: we ask questions about particular technologies, and set about answering these questions using a variety of techniques and data. We are particularly interested in the creation of competitive advantage in low carbon technologies through policy, with an analytic focus on interdependence and geographic focus on the Asia-Pacific. See my interview with Nature Energy on the importance of interdependence in the low carbon energy transition here.
Research and outreach has been supported by the European Commission Strategic Partnership for the Implementation of the Paris Agreement (SPIPA), the Commonwealth Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, the Commonwealth Department of Defence, the Australian Research Council, and various foundations.
Current funded projects include:
Lead Chief Investigator. Supporting Japan's green steel transition through cross-border trade and investment. Philanthropy.
Chief Investigator. Green steel revolution: supply chain futures for Australia, China and the region. Philanthropy.
Chief Investigator. Australia-China links on low-carbon technology transitions. Commonwealth Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT).
Click below to learn more, and get in touch if you’d like to discuss working together.
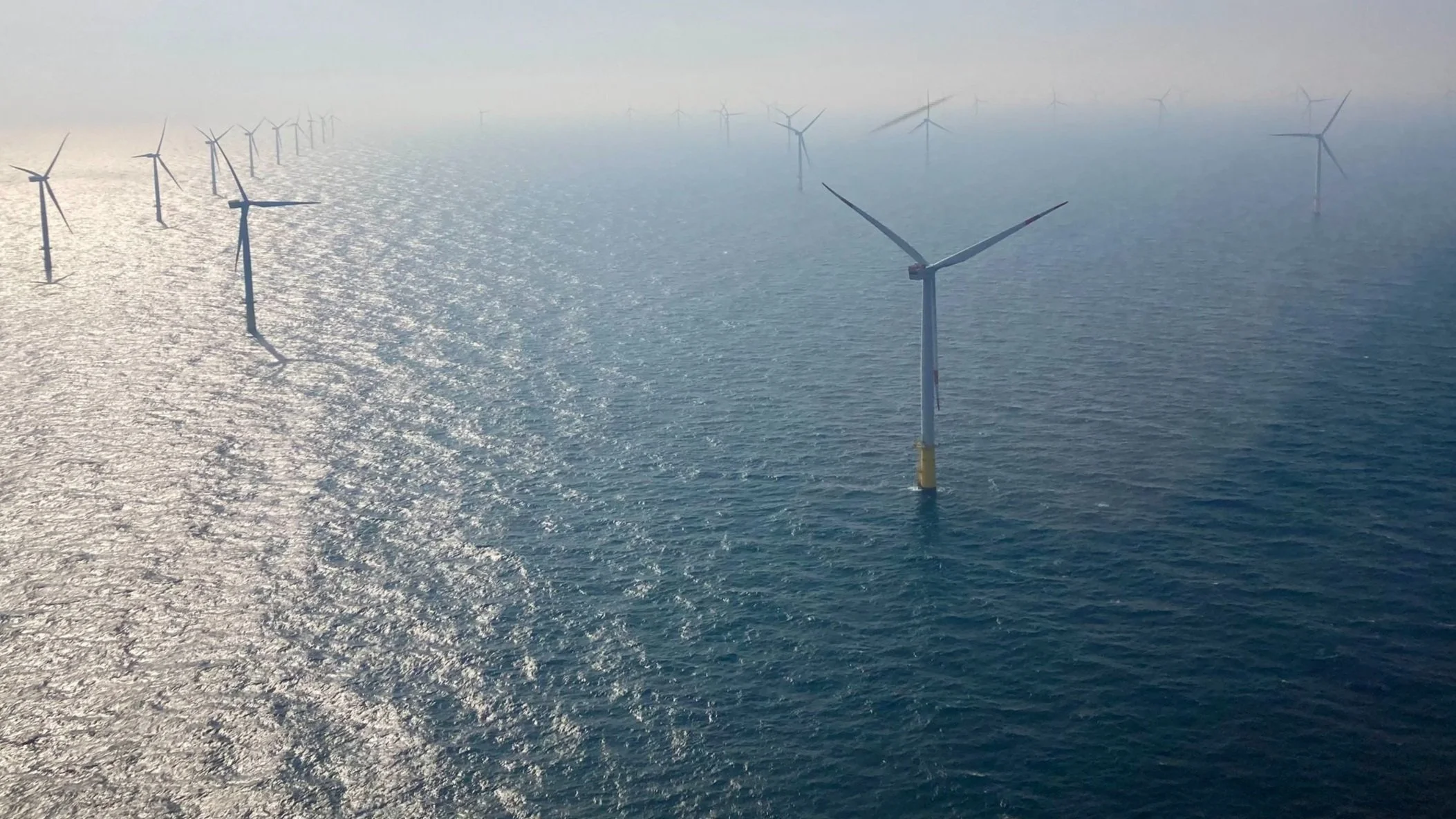
Offshore Wind in the Asia Pacific
Offshore wind has been proposed as a key technology option for decarbonising energy systems in the Asia-Pacific region. We are examining various aspects of offshore wind development and deployment regionally and globally. For more click on the image or here.
Energy Transition Policies
Cross-cutting work that looks at different aspects of policies supporting the low-carbon energy transition. For more click on the image or here.
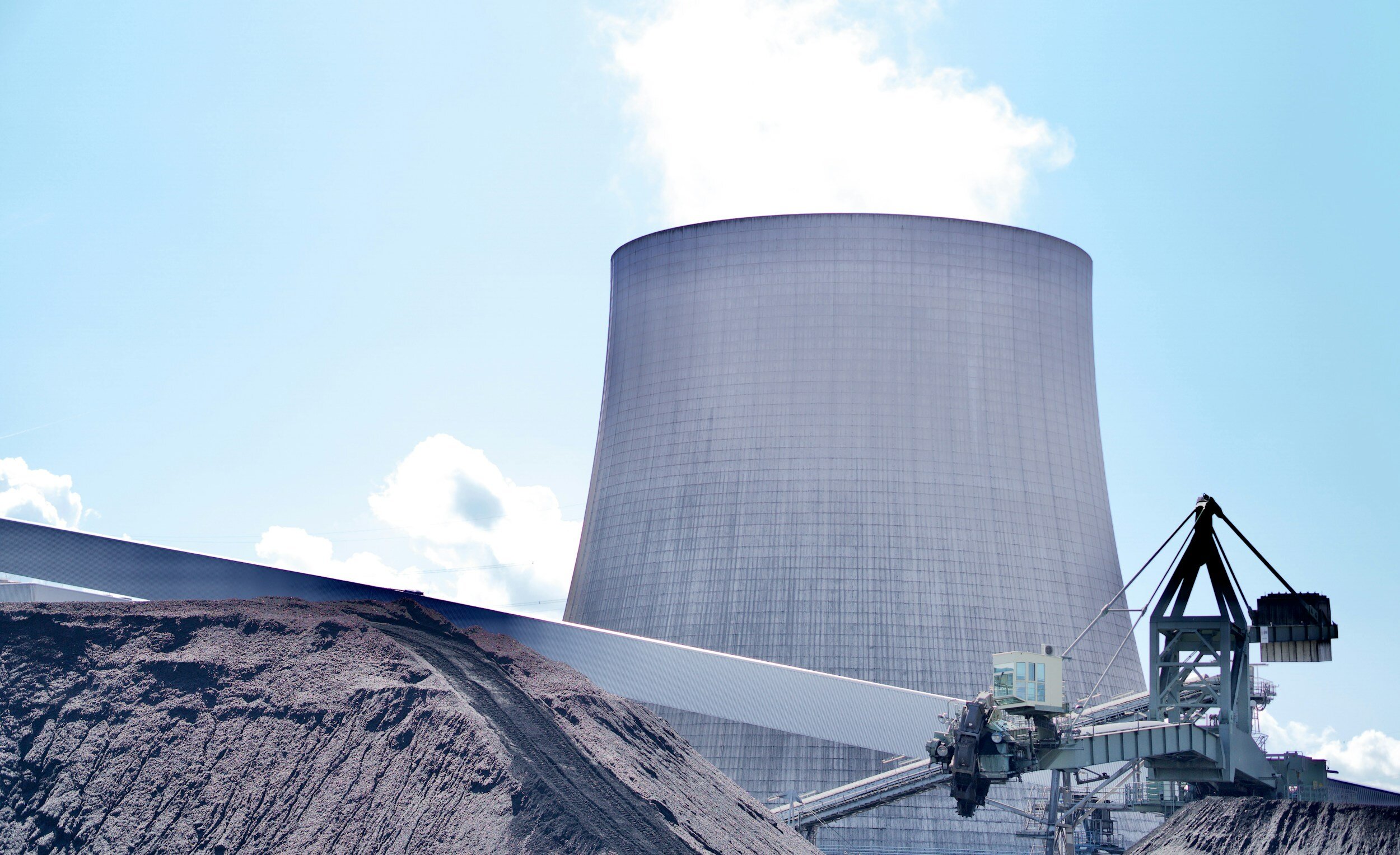
Fossil Fuel Phase-out
In this workstream we are examining various aspects of fossil fuel phase-out in the Asia-Pacific region. Technology options examined include hydrogen and ammonia co-combustion and CCS/CCUS. For more click on the image or here.
Japan Energy Transition
Japan is the 5th largest emitter of CO2 globally and its economy remains largely dependent on fossil fuels. A long-standing area of work charts Japan’s energy transition on a cross-technology and fuel basis.For more click on the image or here.
PhD and Postdoctoral Research Collaborators
Doctoral and postdoctoral students work with us on various aspects of the low carbon energy transition. For more click on the image or here.